Хүннү гүрэн
Агуулга |
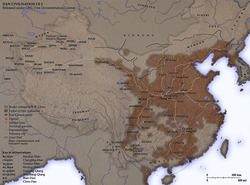
Засаг захиргаа
Хүннү гүрэн засаг захиргааны гурван хэсэгтэй байсны төвийн хэсгийг Шаньюй өөрөө захирч байжээ. Зүүн хэсгийг Жүки ван, баруун хэсгийг Лүли ван захирч байв. Шаньюй болон вангууд түмтүүдийг шууд удирддаг байсан бол түмт нь цаашаа мянгатад, мянгат нь зуутад, зуут нь аравтад хуваагддаг байжээ. Хүннү гүрэн нийт 24 түмттэй байсан мэдээ байна. Энэ тогтолцоог түмтийн тогтолцоо гэдэг. Захиргааны хувьд хамгийн энгийн бөгөөд цэгцтэй хуваарьлалт. Модуны үед Хүннүгийн цэргийн зохион байгуулалт маш боловсронгуй байсныг Хятадын сурвалж бичгүүдэд хангалттай тэмдэглэн үлдээсэн нь бий.Хүчирхэгжил ба Түүх, гадаад харилцаа
1.Хүннү гүрэн МЭӨ 209 – МЭ 93 оршиж байсан. Анх Модунь Шаньюй хан болж байгуулсан. Мандан бадрал: МЭӨ 198 онд Хан улстай найрамдлын гэрээ байгуулж 50 жилийн турш алт мөнгө, тариагаар алба авч байсан, Торгоны их замыг хяналтандаа байлгасан.Хүннү гүрэн нь монгол нутаг дахь анхны төрт улс бөгөөд хамгийн анхны төрийн захиргааг бий болгосон. Албан ёсоор МЭӨ 209 оноос буюу Модун шанью хаан ор сууснаас энэ гүрний он тооллыг тооцдог.Эртний төрт улсуудын нэгд зүй ёсоор оруулдаг.Энэ үед Хүннү гүрэн хүчирхэгжилтийнхээ туйлд хүрч умардад Байгал нуур, урагш Хятадын цагаан хэрэм, баруун тал руугаа Түрэгстан, зүүн тийш одоогийн Ордос хүртэлх өргөн уудам нутгийг эрхшээлдээ оруулж чадсан юм. Одоогийн Хятадын нутагт тэр үед шинээр үүссэн Хань Улс Модун шаньюйд алба гувчуур барьж байсан төдийгүй хааны ургийн гүнжийг түүнд "яньжи" болгон өгч байжээ. Хүннүчүүд байлдааны тактик таа одоогийн тусгай албадын нууц аргыг хэрэглэж байсан нь сонирхол татдаг. Модун шаньюй Хань улсаас ирсэн элчид өөрийн армийг үзүүлэхдээ зөвхөн сул дорой болон хөгшин настай хүмүүсээ харуулаад явуулсан жишээ бий. Модун шаньюй МЭӨ 174 онд таалал болсноос хойш 100 гаруй жил Хүннү нар Төв Азид ноёрхсон хэвээр байв. Манай эриний он тооллын эхэн, манай эриний өмнөх тооллын сүүл үед Хүннү гүрэн дотоодын тэрсэлдээн, гадаадын дайралт довтолгооны нөлөөгөөр умард, өмнөд гэсэн хоёр хэсэгт хуваагдаж, өмнөд нь Хань улсад дагаар орж, өөр хоорондоо дайтах болсон байна. Одоогийн Монголын нутаг дээр байсан өмнөд Хүннү нар умардынхныгаа удаа дараа хиар цохиж, Хань улсын нөмөр нөөлөгт оршиж байсан ч жил ирэх тутам доройтсоор МЭ-ний I зуунд Дунху нарын эрхшээлд орсноор дуусгавар болсон юм.Хүннүгийн шанью өглөө наранд өдөр тэнгэрт, үдэш саранд мөргөдөг байсан гэдэг. Тухайн үед тэнгэр шүтлэг Хүннүгийн төрийн шашин болж байв. Модун шаньюгийн тогтоосон хэв маяг дэлхийн олон оронд 300 жилийн турш хадгалагдаж ирсэн гэж судлаачид үздэг. Хөрш нь өдөж "Сайн морио өг" гэхэд "Ганц мориноос болж хөрштэйгээ муудаж яана" хэмээн сайн морио өгсөн.
/Хүннүгийн Эзэн Шаньюйгийн хэрэглэж байсан алтан Луут бүс. Луут хотоос олдсон /
Хүннүчүүдын гарал үүсэл
Монгол нутагт оршин суусан нүүдэлчин овог аймаг бүр МЭӨ II мянган жилийн үед Хятад оронтой хэлхээ холбоотой байсан тухай товч мэдээ Хятад сурвалж бичигт бий. Их гүйцэд мэдээ гарах болсон нь МЭӨ 4-3 дугаар зууны үе бөгөөд тэр үед Хятадын хойд хязгаарт Хүннү, Дунху гэдэг аймгийн хоёр холбоо бүрэлджээ.Хүннү нарын аймгийн холбоо нь МЭӨ 3-р зууны эцсийн арван онд нэлээд хүчийг олсон нь ардын бослого гарцгааж сурвалжтаны бүлгүүд засгийн эрхийн төлөө хоорондоо тэмцэлдэж байсан хүчирхэг хөрш Хятад орныг сулруулсан явдал нь түүнд зарим талаар дөхөм болжээ. Тэр үед бүрэлдэн байсан Хүннү нарын нийгмийн байгуулал нь анхны хүй нэгдлээс нийгмийн байгуулалд шилжин бүхий үе байжээ. Хүннү нарын аймгийн байгуулалтын улс төрийн хэлбэр нь хожим болтол буюу Хүннү нарын хүчирхэг чадал манай эриний 1-р зууны үед доройтох хүртэл хэвээр байсан цэргийн ардчилал юм. “Цэргийн ардчилал” байгуулал улс төр тогтоох буюу ангит нийгэм тогтохын шууд угтуул нь болдог юм. Хүннү нар эрх мэдэл нь үе улиран , тухайн нэгэн овогт бат оршин, эцгээс хүүд нь шилжүүлдэг байжээ. Аймгийн холбооны тэргүүнд эзэн-шаньюй байдаг агаад МЭӨ 3-р зууны үеэс түүнийг аймаг буюу зонхилогчдын зөвлөлөөр сонгохоо нэгэнт больсон байжээ. Аймгийн сурвалжтан ноёд ялгаран гарч Зонхилогчдын зөвлөл байсаар боловч шийдвэртэй алхам хийдэггүй байв. Өөрийн эцэг Түмэн Шаньюйг алж МЭӨ 209 онд Засгийн эрхийг булаан авсан Модун Шаньюй зонхилогчдоос зөвлөгөө авдаг байсан боловч заримдаа тэднийг тоодоггүйгээр үл барам, хэрэв зонхилогчдыг саналыг нь эс зөвшөөрвөл “толгойгий нь ав” гэж тушаадаг байжээ. Модун Шаньюй хаан ширээ булаасныхаа дараа реформ хийж түүгээрээ хүннү нарын сурвалжтаны үе улирах эрх мэдлийг бэхжүүлжээ. Хүннү нарын мэдэлд орсон газар нутгийг гурав хувааж, нэг хэсэг нь Модун Шаньюйгийн харьяат нарын нутаг болж, нөгөө хоёр хэсэг нь зүүн баруун этгээдийн ноёд: Жуки ван, Лули ван нарын тэргүүлсэн газар болжээ. Зүүн этгээд солгой талаа ахмад тал гэж үздэг байжээ. Ер нь Шаньюйн ширээ залгамжлагч нь зүүн этгээдийн Жуки ван байдаг байжээ. Тэр хоёр ван элдэв цолтой үе залгамжилдаг зонхилогч түмний ноёдыг захирдаг байжээ. Тийм зонхилогч 24 байсны тус бүр нь нэг түмэн морин цэрэгтэй байжээ. Түмний ноёд, мянгат, зуут, аравтын дарга нарыг томилон захирах, тушаах хэргээ гүйцэтгэдэг байв. Хүннү нарын их сурвалжит овог: Хуянь, Лань, хожим гарсан Сюйбу гурав байжээ. Тэдгээр овогоос үе залгамжилдаг ноёд,цэргийн том дарга дэвшин гардаг байлаа.Хүннү нарын сурвалжтаны эрх мэдэл үе залгадаг байсан нь овог аймгийн харилцаа задарч ангит нийгэмд шилжин бүхийн тэмдэг билээ."Сайхан эхнэрээ өг" гэхэд "Ганц хүүхнээс болж хөрштэйгээ муудаж юу хийнэ" хэмээн " эхнэрээ өгсөн, "Хамгийн үржил шимгүй газраа өг" гэхэд "Газар бол төр улсын үндэс. Хэрхэвч өгч үл болно" хэмээн цэрэглэн бос дайтсан Модун Шаньюй өөрий нь золионд явуулж, араас нь дайн дэгдээн хөнөөхийг хүссэн эцгээ егүүтгэж шаньюйг залгамжилсан Монголын анхны төрт улсын хаан билээ. Хүннү шанью -ийн алтан титэм Өвөр Монголын Далан хар уулнаас олдсон
Хүннү шанью -ийн алтан титэм Өвөр Монголын Далан хар уулнаас олдсонАж ахуй ба ахуйн амьдрал
Хүннү нарын аймгийн холбоонд аж ахуйн хэлбэр нь бүдүүн баараг байв. Хүннү нар нүүн аж төрж мал аж ахуй эрхэлдэг байсан тул газар тариаланг огт мэддэггүй байсан гэж сурвалж бичгүүдэд тэмдэглэсэн байдаг. Аймаг бүрийн нүүж буух нутаг нь багцаа тоймтой байжээ. Хүннү нар үхэр бог мал олонтой, зарим нь тэмээ, илжиг, адуу үржүүлдэг байсан байна. Хувцас хүнсний хэрэглээг мал аж ахуйгаас гардаг зүйлээр үндсэнд нь залгуулж, үр тарианы бүтээгдэхүүн, гар үйлдвэрийн эд эдлэл, аймгийн сурвалжтаны гоёл чимгийн юмсыг суурьшмал хөрш орон, гол төлөв Хятад орноос авдаг байжээ. Бичиг үсэг бий болох явдал үйлдвэрлэлийн хөгжиж, анги гарч улс төр бэхжихтэй ямагт холбоотой байдаг. Гэтэл МЭӨ 3-р зууны Хүннү нарт бичиг үсэг байхгүй байсан нь тэр үед хүннү нар анги хөгжсөн нийгэм, гүйцэд бүрэлдэн тогтсон улс төртэй байгаагүйг гэрчилж байна. Анхны хүй нэгдлийн харьцаанаас ангит нийгэмд шилжсэн цагийн нийгмийн хөгжлийн шатанд байсан хүннү нарт дайн, байнгын ажил нь байжээ. Энэ бол гагцхүү Хүннү нарт ч хамаатай бус, хөгжлийн тийм шатанд байсан бусад аймагт ч ийм шинж илэрдэг байсан юм. Хүннү нарын Модун Шаньюй, түүний хойчийг залгагсад хөрш орнуудтайгаа сэгхийлгүй дайтдаг байжээ. Модун МЭӨ 209 онд дунху аймгуудыг гэнэт довтолж дийлээд, газар хүн хөрөнгий нь түрэмгийлэн авчээ. Нэг хэсэг дунху нар Модунд захирагдах болж , түүнд захирагдахгүй гэсэн нөгөө хэсэг дунху нар нь хойд зүгт зугатаж, Онон, Хэрлэн, Өргөнө мөрний газрыг эзлэн суужээ. Дунхугийн гол олонх нь Ляо /Луух/ голын эхэнд шилжин нүүжээ. Модун цаашдаа баруун зүгт Юэчжи аймгийг бут цохиж, өмнө зүг Ордосоор нутагласан аймгуудыг эзлэн бүр Цинь улсын /МЭӨ 246-207 оны/ үед Хятадын жанжин Мень Тяний, хүннү нараас булаан авсан газрыг эргүүлэн аваад, хойд зүгийн хэд хэдэн аймгийг эзлэн авчээ. Хүннү нарын байн байн дайтаж байсан олон дайн нь үе залгадаг сурвалжтан ялгаран гарч эрх мэдлээ булаацалдан, эрх мэдлээ бүх аймгийн эсрэг тавихад том үүрэгтэй байжээ. Модунгийн үед хүннү нарын аймгийн холбоо нь өргөн уудам нутгийг эзэлж маш хүчирхгийн туйлд хүрчээ. Хүннү нарын нутгийн хил нь баруун зүгт Дорнод-Туркестаны хот-улсууд, зүүн зүгт дунху аймгууд нутаглаж байсан Ляо голын эхэн газар, өмнө зүгт хятад /одоогийн Шаньси, Ордос/ нутаг бөгөөд Хятад Хүннү нарын хил нь Түмэн газрын цагаан хэрэм дагуу байж, хойд зүгт хүннү нарын нутаг Байгаль нуур хүрч байлаа. Дээрмийн дайн хийж нутгаа тэлж өргөтгөсөн хүннү нарын амжилтанд нэг талаар бусад нүүдэлч нарын нэлээд сул дорой байсан гадаад зохимжтой нөхцөл, Хятад орон дахь дажин хямрал ихтэй байснаар тийм завшаан нээгдэж, нөгөө талаар тэр амжилтанд хүннү нар эртний хорезмуудын жишээгээр хүнд зэр зэвсэгт морин цэрэг хэрэглэх болж бас хүннү нарын цэрэг аймгийн байгуулалт тус дөхөм болжээ. Зэр зэвсэгт гарсан шинэ зүйл нь чин бат бэгтэр хуягийг хүн морь хоёрт хэрэглэж, бас мориноос гинжээр торгосон довтлох урт жад хэрэглэсэн явдал даруй мөн. Хүннү нарын холбооны цэрэг аймгийн байгуулалт нь дээр заасан ёсоор бүх аймгаа байлдааны нэгж, арван, зуун, мянган, түмэн гэдэн хуваариар хувааж, цэргийн сургууль үргэлж хийлгэдэг байжээ. Тийм байгууламж нь цэргийн хүч зузаатгах бэлтгэлтэй болж, аймгийн бүх эрчүүдийг байнгын цэрэг болгосон гэсэн үг юм. Модун Шаньюйн байлдан дагууллын улмаас хүннү нарын аймгийн холбоо нь монгол, хамнига, тюрк гарлын элдэв аймгийг хамран багтаажээ. Өмнө зүгт хүннү нарын захиргаанд нэг хэсэг хятад хүн байжээ. Хүннү нарын үргэлжийн довтолгоонд эрсдэн нэрвэгдсэн Хятадын Хань улс хүннү нарын аргадаж үе үе бэлэг сэлт барьдаг байсан нь нэг ёсны алба байсан гэдэг. Модун Шаньюйг нас барснаас хойш / МЭӨ 174 онд/ дараачинй шаньюй нарын цагт 100 гаруй жилд хүнүү нарын холбооны дотоод аймгууд хоорондоо тулалдаж бас Хятадтай тэмцэлдэж байлаа. Хятадад харьяалагдаж Дунхугийн ухуань, Сяньби аймагтай тэмцэлдэн хүч нь суларсан өвөр хүннү нар монгол нутагт суусаар байжээ.Өвөр хүннү нар МЭ 215 он хүртэл монгол оронд мэдэгдэхүйц улс төрийн роль гүйцэтгэж байгаад түүний дараачаар өвөр хүннү нарын нэг хэсэг нь бусад аймгийн дунд шингэж нөгөө хэсэг нь умард хятадын зүгт нүүн шилжиж аажмаар уусан шингэжээ. МЭ 4-5 дугаар зуунд холбогдох Нангиадын түүх шаштирт тэмдэглагдсэнээр өвөр Хүннү нарын үр сад нэг бус удаа бослого самуун өдүүлж, Нангиадын Сүй улсын хаан ширээг Ан-Лу-шан хэмээх Хүн угсааны этгээд булааж хаан суув хэмээн дурьдсан байдаг байна.Уналт
Хүннү гүрний захиргаанд байсан, дээр өгүүлсэн Дун-Ху нар буюу Сяньби нар Хан улстай холбоо тогтоов, МЭӨ 48 онд хаан ширээний төлөөх тэмцэл гарч Ар, Өвөр гэж 2 хуваагдан өмнөд хэсэг Хан улсын харъяат болов. Гадаадын улсууд довтолсон.Манай эриний 85, 87 онд Сяньби аймаг ар хүннү нарыг бут ниргэсэн учир тэд дахин сэхэж чадаагүй юм. Өвөр хүннү нар хятад цэрэгтэй хүч хавсран ар хүннү нарыг хэд хэдэн удаа хавчин тулж тэднийг бут цохижээ. Ар хүннү нар 93 онд аймгийн бие даасан нэгдэл болон тогтохоо больж нэг хэсэг нь хядуулж, амь гарсан нэг бум гаруй өрх айл, сяньби аймагт нэгдэж тэдний аймгийн нэртэй болжээ.Нангиадууд 3000 жил турш нүүдэлчидтэй тэмцэхдээ хязгаарлагддмал орон зайд л түр хүчирхэгжих чадалтайгаа харуулжээ.Турфанд бэхэжсэн Хятадууд Хүнчүүдийн баруун зүгийн улсуудтай харилцах замыг тасалсанхийгээд Нангиадын хаадын он удаан жил үргэлжилсэн хутган үймүүлэх бодлогын үр дүнд дотоодын зөрчлөөс болж МЭӨ I зуун гэхэд Хүннүчүүд ихэд сульдсан байлаа. Ар Хүннүгийн Жижиг шаньюйд туслуулахаар Парфянчууд баруун зүгт хийсэн дайныхаа явцад Крассын гурвын холбооноос олзолсон легионыг илгээсэн байдаг юм. Жижиг шаньюйн бэхлэлтийг хамгаалж байсан ромчууд том дөрвөлжин бамбайгаа өргөн, богино жадаа сунган довтолоход Хятадууд өвөр Хүннү нартай хүч хавсран хатуу холхивч нумаар нягт жагсаалыг нь сарниулаад морин цэргээр хядчихсан байдаг юм. Жижиг шаньюй бууж өгөлгүй тулалдсаар алуулсан ба хүннү нар Дундад азийн гүн рүү ухран зугтсан байна. Өмнөдийнхөндөө бут цохигдон олон хэсэг болж тарж бутран, хөөгдөн нүүдэллэцгээсэн ба тэд одоогийн Европт хүрч очсон Кангю аймагтай холбоо тогтоон хэсэг зуур хүчирхэгжиж өрнө дахиныг чичрүүлж байсан түүх бий.Археологийн дурсгал
НТӨ III - НТ II зуун хүртэлх хугацаанд Төв Азийн өргөн уудам тал нутагт Хүннү нар нүүдэллэн амьдарч, төр улсаа цогцлоон байсны нотолгоо археологийн дурсгалууд Хүннүгийн үндсэн нутаг болох Монгол улс, ОХУ-ын Өвөр Байгал, Тува, БНХАУ-ын Өвөр Монгол, Шинжан Уйгарын өөртөө засах орон, Ганьсу, Хөх нуур мужийн нутгаас олддог. Хүннүгийн археологийн дурсгалыг булш оршуулгын дурсгал, хот суурин, хадны зураг хэмээн ангилан үздэг юм.Xiongnu
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Hunnu)
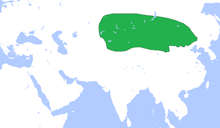
Territory of the Xiongnu (green) which includes Mongolia, Western Manchuria, Tarim Basin, East Kazakhstan, East Kyrgyzstan, Inner Mongolia, Gansu circa 250 BC
The identity of the ethnic core of Xiongnu has been a subject of varied hypotheses, because only a few words, mainly titles and personal names, were preserved in the Chinese sources. Proposals by scholars include Mongolic, Turkic, Yeniseian,[2][3] Tocharian, Iranian,[4][5] and Uralic.[6] They also possibly practiced Tengriism.[7][8] The name Xiongnu may be cognate to the name Huns, but the evidence for this is controversial.[3][9]
Chinese sources from the 3rd century BC report them as having created an empire under Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC.[10] This empire stretched beyond the borders of modern-day Mongolia. After defeating the previously dominant Yuezhi in the 2nd century BC, Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of central and eastern Asia. They were active in regions of what is now southern Siberia, Mongolia, western Manchuria, and the Chinese provinces of Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Relations between early Chinese dynasties and the Xiongnu were complex, with repeated periods of military conflict and intrigue alternating with exchanges of tribute, trade, and marriage treaties.
Contents[hide]
|
[edit] History
See also: History of the Han Dynasty
[edit] Outline
From 209 BC Modu Chanyu united the steppe tribes north of China into the first large Steppe empire. Soon the new Han Dynasty was paying them tribute. From 133 BC Emperor Wu adopted an aggressive policy and pushed Chinese power west and north. Around 50 AD, following the second Xiongnu civil war, the southern Xiongnu submitted to China while the Northern Xiongnu remained independent. By around 100 AD the Xiongnu had been replaced by the Xianbe. Xiongnu remnants and descendents remained on the northern frontier and in the period around 250-450 AD they formed several short-lived dynasties in North China.[edit] Early
An early reference to the Xiongnu was by Sima Qian who wrote about the Xiongnu in the Shiji (ca. 100 BC), drawing a distinct line between the settled Huaxia people (Chinese) to the pastoral nomads (Xiongnu), characterizing it as two polar groups in the sense of a civilization versus an uncivilized society.[11] Sources from the pre-Han eras often classified the Xiongnu as the Hu people, even though this was more a blanket term for nomadic people in general; it only became an ethnonym for the Xiongnu during the Han.[12]Ancient China often came in contact with was described as the "Hsien-yün" and the "Jung" nomadic people. In later Chinese historiography, some groups of these peoples were believed to be the possible progenitors of the Xiongnu people.[12] These nomadic people often had repeated military confrontations with the Chinese dynasties of the Shang and especially the Zhou, who often conquered and enslaved the nomads in an expansion drift.[12] During the Warring States period, the Chinese armies from the Qin, Zhao, and Yan states were encroaching and conquering various nomadic territories that were inhabited by the Xiongnu and other Hu peoples.[13]
The Chinese Qin empire was set on preemptively attacking the Xiongnu and expanding their territory at the expense of the Xiongnu.[14] In 215 BC, Qin Shi Huang sent General Meng Tian to conquer the Xiongnu and drive them from the Ordos region, which he did later that year.[15] After the catastrophic defeat at the hands of General Meng Tian, the Xiongnu leader Touman was forced to flee far into the Mongolian Plateau.[16] The Qin empire became a threat to the Xiongnu, which ultimately led to the reorganization of the many tribes into a confederacy.[14]
[edit] State formation
After forging internal unity, Modu expanded the empire on all sides. To the north he conquered a number of nomadic peoples, including the Dingling of southern Siberia. He crushed the power of the Donghu of eastern Mongolia and Manchuria, as well as the Yuezhi in the Hexi Corridor of Gansu where his son Jizhu made a cup out of the skull of the Yuezhi king. Modu also reoccupied all the lands previously taken by the Qin general Meng Tian. Under Modu's leadership, the Xiongnu threatened the Han Dynasty, almost causing Liu Bang to lose his throne in 200 BCE.[19] By the time of Modu's death in 174 BC, the Xiongnu had driven the Yuezhi from the Hexi Corridor, killing the Yuezhi king in the process and asserting their presence in the Western Regions of Xinjiang.
They were recognized as the most prominent of the nomads bordering the Chinese Han empire.[19]
[edit] Xiongnu hierarchy
After Modu, later leaders formed a dualistic system of political organisation with the left and right branches of the Xiongnu divided on a regional basis. The chanyu or shan-yü – supreme ruler equivalent to the Chinese "Son of Heaven" – exercised direct authority over the central territory. Longcheng (蘢城), near Khöshöö Tsaidam in Mongolia, became the annual meeting place and served as the Xiongnu capital.[20]The ruler of the Xiongnu was called the Chanyu.[21] Under him were the "Wise Kings (Tuqi Kings) of the Left and Right."[21] The Wise King of the Left was normally the heir presumptive.[21] Next lower in the hierarchy came more officials in pairs of left and right: the guli (kuli, 'kings'), the army commanders, the great governors, the dunghu (tung-hu), the gudu (ku-tu). Beneath them came the commanders of detachments of one thousand, of one hundred, and of ten men. This nation of nomads, a people on the march, was organized like an army.[22] ("Chanyu", in Chinese Chengli Gutu Shanyü, "Majesty Son of Heaven" might be a loanword from Turko-Mongol Tengri, The Heaven. "Wise", in Chinese 'tuqi' or 'tu-ch'i, is perhaps from Turkic 'doghri', straight, faithful.[23])
Yap,[24] apparently describing the early period, places the Chanyu's main camp north of Shanxi with the Wise King of the Left holding the area north of Beijing and the Wise King of the Right holding the Ordos Loop area as far as Gansu. Grousset,[25] probably describing the situation after the Xiongnu had been driven north, places the Chanyu on the upper Orkhon near where Genghis Khan would later establish his capital of Karakorum. The Wise King of the Left lived in the east, probably on the high Kherlen. The Wise King of the Right lived in the west, perhaps near present day Uliastai in the Khangai Mountains.
[edit] The marriage treaty system
In the winter of 200 BC, following a siege of Taiyuan, Emperor Gaozu personally led a military campaign against Modun. At the Battle of Baideng, he was ambushed reputedly by 300,000 elite Xiongnu cavalry. The emperor was cut off from supplies and reinforcements for seven days, only narrowly escaping capture.After the defeat at Pingcheng, the Han emperor abandoned a military solution to the Xiongnu threat. Instead, in 198 BC, the courtier Liu Jing (劉敬) was dispatched for negotiations. The peace settlement eventually reached between the parties included a Han princess given in marriage to the chanyu (called heqin Chinese: 和親; literally "harmonious kinship"); periodic gifts to the Xiongnu of silk, liquor, and rice; equal status between the states; and the Great Wall as mutual border.
This first treaty set the pattern for relations between the Han and the Xiongnu for sixty years. Up to 135 BC, the treaty was renewed no less than nine times, each time with an increase in the "gifts". In 192 BC, Modun even asked for the hand of Emperor Gao's widow Empress Lü Zhi. His son and successor, the energetic Jiyu, known as the Laoshang Chanyu, continued his father's expansionist policies. Laoshang succeeded in negotiating with Emperor Wen terms for the maintenance of a large scale government sponsored market system.
While the Xiongnu benefited handsomely, from the Chinese perspective marriage treaties were costly, humiliating, and ineffective. Laoshang showed that he did not take the peace treaty seriously. On one occasion his scouts penetrated to a point near Chang'an. In 166 BC he personally led 140,000 cavalry to invade Anding, reaching as far as the imperial retreat at Yong. In 158 BC, his successor sent 30,000 cavalry to attack the Shang commandery and another 30,000 to Yunzhong.
[edit] War with Han Dynasty
Main article: Han–Xiongnu War
While Han China was making preparations for a military confrontation from the reign of Emperor Wen, the break did not come until 133 BC, following an abortive trap to ambush the chanyu at Mayi. By that point the empire was consolidated politically, militarily and economically, and was led by an adventurous pro-war faction at court. In that year, Emperor Wu reversed the decision he had made the year before to renew the peace treaty.
Full-scale war broke out in autumn 129 BC, when 40,000 Chinese cavalry made a surprise attack on the Xiongnu at the border markets. In 127 BC, the Han general Wei Qing retook the Ordos. In 121 BC, the Xiongnu suffered another setback when Huo Qubing led a force of light cavalry westward out of Longxi and within six days fought his way through five Xiongnu kingdoms. The Xiongnu Hunye king was forced to surrender with 40,000 men. In 119 BC both Huo and Wei, each leading 50,000 cavalrymen and 100,000 footsoldiers (in order to keep up with the mobility of the Xiongnu, many of the non-cavalry Han soldiers were mobile infantrymen who traveled on horseback but fought on foot), and advancing along different routes, forced the chanyu and his court to flee north of the Gobi Desert.[26] Major logistical difficulties limited the duration and long-term continuation of these campaigns. According to the analysis of Yan You (嚴尤), the difficulties were twofold. Firstly there was the problem of supplying food across long distances. Secondly, the weather in the northern Xiongnu lands was difficult for Han soldiers, who could never carry enough fuel.[27] According to official reports, the Xiongnu lost 80,000 to 90,000 men. And out of the 140,000 horses the Han forces had brought into the desert, fewer than 30,000 returned to China.
As a result of these battles, the Chinese controlled the strategic region from the Ordos and Gansu corridor to Lop Nor. They succeeded in separating the Xiongnu from the Qiang peoples to the south, and also gained direct access to the Western Regions.
Ban Chao, Protector General (都護; Duhu) of the Han Dynasty embarked with an army of 70,000 men in a campaign against the Xiongnu insurgents who were harassing the trade route we now know as the Silk Road. His successful military campaign saw the subjugation of one Xiongnu tribe after another. Ban Chao also sent an envoy named Gan Ying to Daqin (Rome). Ban Chao was created the Marquess of Dingyuan (定遠侯, i.e., "the Marquess who stabilized faraway places") for his services to the Han Empire and returned to the capital Loyang at the age of 70 years old and died there in the year 102. Following his death, the power of the Xiongnu in the Western Regions increased again, and the emperors of subsequent dynasties were never again able to reach so far to the west.
[edit] The First Xiongnu Civil War (60–53 BC)
When a Chanyu died, power could pass to his younger brother if his son was not of age. This system, which can be compared to Gaelic tanistry, normally kept an adult male on the throne, but could cause trouble in later generations when there were several lineages that might claim the throne. When the 12th Chanyu died in 60BC, power was taken by Woyanqudi, a grandson of the 12th Chanyu's cousin. Being something of a usurper, he tried to put his own men in power, which only increased the number of his enemies. The 12th Chanyu's son fled east and, in 58BC, revolted. Few would support Woyanqudi and he was driven to suicide, leaving the rebel son, Huhanye, as the 14th Chanyu. The Woyanqudi faction then set up his brother, Tuqi, as Chanyu (58BC). In 57BC three more men declared themselves Chanyu. Two dropped their claims in favor of the third who was defeated by Tuqi in that year and surrendered to Huhanye the following year. In 56BC Tuqi was defeated by Huhanye and committed suicide, but two more claimants appeared: Runzhen and Huhanye's elder brother Zhizhi Chanyu. Runzhen was killed by Zhizhi in 54BC, leaving only Zhizhi and Huhanye. Zhizhi grew in power, and, in 53BC, Huhanye moved south and submitted to the Chinese. Huhanye used Chinese support to weaken Zhizhi, who gradually moved west. In 49BC a brother to Tuqi set himself up as Chanyu and was killed by Zhizhi. In 36BC Zhizhi was killed by a Chinese army while trying to establish a new kingdom in the far west near Lake Balkhash.[edit] Tributary relations with the Han
Huhanye sent his son, the "wise king of the right" Shuloujutang, to the Han court as hostage. In 51 BC he personally visited Chang'an to pay homage to the emperor on the Lunar New Year. On the financial side, Huhanye was amply rewarded in large quantities of gold, cash, clothes, silk, horses and grain for his participation. Huhanye made two more homage trips, in 49 BC and 33 BC; with each one the imperial gifts were increased. On the last trip, Huhanye took the opportunity to ask to be allowed to become an imperial son-in-law. As a sign of the decline in the political status of the Xiongnu, Emperor Yuan refused, giving him instead five ladies-in-waiting. One of them was Wang Zhaojun, famed in Chinese folklore as one of the Four Beauties.
When Zhizhi learned of his brother's submission, he also sent a son to the Han court as hostage in 53 BC. Then twice, in 51 BC and 50 BC, he sent envoys to the Han court with tribute. But having failed to pay homage personally, he was never admitted to the tributary system. In 36 BC, a junior officer named Chen Tang, with the help of Gan Yanshou, protector-general of the Western Regions, assembled an expeditionary force that defeated him at the Battle of Zhizhi and sent his head as a trophy to Chang'an.
Tributary relations were discontinued during the reign of Huduershi (18 AD–48), corresponding to the political upheavals of the Xin Dynasty in China. The Xiongnu took the opportunity to regain control of the western regions, as well as neighbouring peoples such as the Wuhuan. In 24 AD, Hudershi even talked about reversing the tributary system.
[edit] Northern Xiongnu
The Xiongnu's new power was met with a policy of appeasement by Emperor Guangwu. At the height of his power, Huduershi even compared himself to his illustrious ancestor, Modu. Due to growing regionalism among the Xiongnu, however, Huduershi was never able to establish unquestioned authority. When he designated his son as heir apparent (in contravention of the principle of fraternal succession established by Huhanye), Bi, the Rizhu king of the right, refused to attend the annual meeting at the chanyu's court.As the eldest son of the preceding chanyu, Bi had a legitimate claim to the succession. In 48, two years after Huduershi's son Punu ascended the throne, eight Xiongnu tribes in Bi's powerbase in the south, with a military force totalling 40,000 to 50,000 men, acclaimed Bi as their own chanyu. Throughout the Eastern Han period, these two groups were called the southern Xiongnu and the northern Xiongnu, respectively.
Hard pressed by the northern Xiongnu and plagued by natural calamities, Bi brought the southern Xiongnu into tributary relations with Han China in 50. The tributary system was considerably tightened to keep the southern Xiongnu under Han supervision. The chanyu was ordered to establish his court in the Meiji district of Xihe commandery. The southern Xiongnu were resettled in eight frontier commanderies. At the same time, large numbers of Chinese were forced to migrate to these commanderies, where mixed settlements began to appear. The northern Xiongnu were dispersed by the Xianbei in 85 and again in 89 by the Chinese during the Battle of Ikh Bayan, in which the last Northern Chanyu was defeated and fled over to the north west with his subjects.
[edit] Southern Xiongnu
Towards the end of the Eastern Han, the southern Xiongnu were drawn into the rebellions then plaguing the Han court. In 188, the chanyu was murdered by some of his own subjects for agreeing to send troops to help the Han suppress a rebellion in Hebei – many of the Xiongnu feared that it would set a precedent for unending military service to the Han court. The murdered chanyu's son Yufuluo, entitled Chizhisizhu (持至尸逐侯), succeeded him, but was then overthrown by the same rebellious faction in 189. He travelled to Luoyang (the Han capital) to seek aid from the Han court, but at this time the Han court was in disorder from the clash between Grand General He Jin and the eunuchs, and the intervention of the warlord Dong Zhuo. The chanyu had no choice but to settle down with his followers in Pingyang, a city in Shanxi. In 195, he died and was succeeded by his brother Hucuquan.
In 216, the warlord-statesman Cao Cao detained Hucuquan in the city of Ye, and divided his followers in Shanxi into five divisions: left, right, south, north, and centre. This was aimed at preventing the exiled Xiongnu in Shanxi from engaging in rebellion, and also allowed Cao Cao to use the Xiongnu as auxiliaries in his cavalry. Eventually, the Xiongnu aristocracy in Shanxi changed their surname from Luanti to Liu for prestige reasons, claiming that they were related to the Han imperial clan through the old intermarriage policy.
[edit] Post-Han Dynasty
After Hucuquan, the Xiongnu were partitioned into five local tribes. The complicated ethnic situation of the mixed frontier settlements instituted during the Eastern Han had grave consequences, not fully apprehended by the Chinese government until the end of the 3rd century. By 260, Liu Qubei had organized the Tiefu confederacy in the north east, and by 290, Liu Yuan was leading a splinter group in the south west. At that time, non-Chinese unrest reached alarming proportions along the whole of the Western Jin frontier.[edit] Liu Yuan's Northern Han (304–318)
In 304 the sinicised Liu Yuan, a grandson of Yufuluo Chizhisizhu stirred up descendants of the southern Xiongnu in rebellion in Shanxi, taking advantage of the War of the Eight Princes then raging around the Western Jin capital Luoyang. Under Liu Yuan's leadership, they were joined by a large number of frontier Chinese and became known as Bei Han. Liu Yuan used 'Han' as the name of his state, hoping to tap into the lingering nostalgia for the glory of the Han dynasty, and established his capital in Pingyang. The Xiongnu use of large numbers of heavy cavalry with iron armour for both rider and horse gave them a decisive advantage over Jin armies already weakened and demoralised by three years of civil war. In 311, they captured Luoyang, and with it the Jin emperor Sima Chi (Emperor Huai). In 316, the next Jin emperor was captured in Chang'an, and the whole of north China came under Xiongnu rule while remnants of the Jin dynasty survived in the south (known to historians as the Eastern Jin).[edit] Liu Yao's Former Zhao (318–329)
In 318, after suppressing a coup by a powerful minister in the Xiongnu-Han court (in which the Xiongnu-Han emperor and a large proportion of the aristocracy were massacred), the Xiongnu prince Liu Yao moved the Xiongnu-Han capital from Pingyang to Chang'an and renamed the dynasty as Zhao (Liu Yuan had declared the empire's name Han to create a linkage with Han Dynasty—to which he claimed he was a descendant, through a princess, but Liu Yao felt that it was time to end the linkage with Han and explicitly restore the linkage to the great Xiongnu chanyu Maodun, and therefore decided to change the name of the state. However, this was not a break from Liu Yuan, as he continued to honor Liu Yuan and Liu Cong posthumously.) (it is hence known to historians collectively as Han Zhao). However, the eastern part of north China came under the control of a rebel Xiongnu-Han general of Jie (probably Yeniseian) ancestry named Shi Le. Liu Yao and Shi Le fought a long war until 329, when Liu Yao was captured in battle and executed. Chang'an fell to Shi Le soon after, and the Xiongnu dynasty was wiped out. North China was ruled by Shi Le's Later Zhao dynasty for the next 20 years.However, the "Liu" Xiongnu remained active in the north for at least another century.
[edit] Tiefu and Xia (260–431)
The northern Tiefu branch of the Xiongnu gained control of the Inner Mongolian region in the 10 years between the conquest of the Tuoba Xianbei state of Dai by the Former Qin empire in 376, and its restoration in 386 as the Northern Wei. After 386, the Tiefu were gradually destroyed by or surrendered to the Tuoba, with the submitting Tiefu becoming known as the Dugu. Liu Bobo, a surviving prince of the Tiefu fled to the Ordos Loop, where he founded a state called the Xia (thus named because of the Xiongnu's supposed ancestry from the Xia dynasty) and changed his surname to Helian (赫連). The Helian-Xia state was conquered by the Northern Wei in 428–431, and the Xiongnu thenceforth effectively ceased to play a major role in Chinese history, assimilating into the Xianbei and Han ethnicities.Tongwancheng (meaning "Unite All Nations") was the capital of the Xia (Sixteen Kingdoms), whose rulers claimed descent from Modu Chanyu.
The ruined city was discovered in 1996[28] and the State Council designated it as a cultural relic under top state protection. The repair of the Yong'an Platform, where Helian Bobo, emperor of the Da Xia regime, reviewed parading troops, has been finished and restoration on the 31-meter-tall turret will begin soon.[29][30] There are hopes that Tongwancheng may achieve UNESCO World Heritage status.[31]
[edit] Juqu and Northern Liang (401–460)
The Juqu were a branch of the Xiongnu. Their leader Juqu Mengxun took over the Northern Liang by overthrowing the former puppet ruler Duan Ye. By 439, the Juqu power was destroyed by the Northern Wei. Their remnants were then settled in the city of Gaochang before being destroyed by the Rouran.[edit] Interpretation
Barfield [32] attempted to interpret Xiongnu history as well as narrate it. He made the following points. The Xiongnu confederation was unusually long-lived for a steppe empire. The purpose of raiding China was not simply booty, but to force the Chinese to pay regular tribute. The power of the Xiongnu ruler was based on his control of Chinese tribute which he used to reward his supporters. The Han and Xiongnu empires rose at the same time because the Xiongnu state depended on Chinese tribute. A major Xiongnu weakness was the custom of lateral succession. If a dead ruler's son was not old enough to take command, power passed to the late ruler's brother. This worked in the first generation but could lead to civil war in the second generation. The first time this happened, in 60 BC, the weaker party adopted what Barfield calls the 'inner frontier strategy.' They moved south and submitted to China and then used Chinese resources to defeat the Northern Xiongnu and re-establish the empire. The second time this happened, about 47 AD, the strategy failed. The southern ruler was unable to defeat the northern ruler and the Xiongnu remained divided.[edit] Ethno-linguistics
| Pronunciation of 匈 Source: http://starling.rinet.ru | |
|---|---|
| Preclassic Old Chinese: | sŋoŋ |
| Classic Old Chinese: | [ŋ̊oŋ] |
| Postclassic Old Chinese: | hoŋ |
| Middle Chinese: | xöuŋ |
| Modern Mandarin: | [ɕɥʊ́ŋ] |
The supposed Old Chinese sound of the first character (匈) has a possible similarity with the name "Hun" in European languages. The second character (奴) appears to have no parallel in Western terminology. Whether the similarity is evidence of kinship or mere coincidence is hard to tell. It could lend credence to the theory that the Huns were in fact descendants of the Northern Xiongnu who migrated westward, or that the Huns were using a name borrowed from the Northern Xiongnu, or that these Xiongnu made up part of the Hun confederation. As in the case of the Rouran with the Avars, oversimplifications have led to the Xiongnu often being identified with the Huns, who populated the frontiers of Europe. The connection started with the writings of the 18th century French historian de Guignes, who noticed that a few of the barbarian tribes north of China associated with the Xiongnu had been named "Hun" with varying Chinese characters. This theory remains at the level of speculation, although it is accepted by some scholars, including Chinese ones. DNA testing of Hun remains has not proven conclusive in determining the origin of the Huns.
Although the phonetic evidence is inconclusive, new results from Central Asia might shift the balance in favor of a political and cultural link between the Xiongnu and the Huns. The Central Asian sources of the 4th century translated in both direction Xiongnu by Huns (in the Sogdian Ancient Letters, the Xiongnu in Northern China are named xwn, while in the Buddhist translations by Dharmarakhsa Huna of the Indian text is translated Xiongnu). The Hunnic cauldrons are similar to the Ordos Xiongnu ones. Moreover, both in Hungary and in the Ordos they were found buried in river banks.[33]
[edit] Turkic theories
See also: Turkic languages
Since the early 19th century, Western scholars have proposed various language families or subfamilies as the affines of the language of the Xiongnu. Proponents of the Turkic languages included E.H. Parker, Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat, Julius Klaproth, Kurakichi Shiratori, Gustaf John Ramstedt, Annemarie von Gabain, and Omeljan Pritsak.[34] Some sources say the ruling class was proto-Turkic,[35][36] while others suggest it was proto-Hunnic.Just as in the 7th century Chinese History of Northern Dynasties[37] and the Book of Zhou,[38] an inscription in the Iranian language, Sogdian, reports the Turks to be a subgroup of the Huns.[39][40][41][42][43] Henning (1948) also exorcised the perpetual debate about equivalency of the numerous Chinese phonetic renditions of the word Hun and the Huns known from non-Chinese sources, by demonstrating an alphabetical form of the word coded in the Chinese as Xiongnu.
[edit] Iranic theories
See also: Iranian languages
Among scholars who proposed an Iranic origin for the Xiongnu are H.W. Bailey (1985)[44] and János Harmatta (1999), who believe that the Xiongnu confederation consisted of 24 tribes, controlling a nomadic empire with a strong military organization, and that "their loyal tribes and kings (shan-yü) bore Iranian names and all the Hsiung-nu words noted by the Chinese can be explained from an Iranian language of the Saka type. . . . It is therefore clear that the majority of Hsiung-nu tribes spoke an Eastern Iranian language".[4] Jankowski concurs.[5][edit] Yeniseian theories
See also: Yeniseian languages
Lajos Ligeti was the first to suggest that the Xiongnu spoke a Yeniseian language. In the early 1960s Edwin Pulleyblank was the first to expand upon this idea with credible evidence. In 2000, Alexander Vovin reanalyzed Pulleyblank's argument and found further support for it by utilizing the most recent reconstruction of Old Chinese phonology by Starostin and Baxter and a single Chinese transcription of a sentence in the language of the Jie (a member tribe of the Xiongnu confederacy). Previous Turkic interpretations of the aforementioned sentence do not match the Chinese translation as precisely as using Yeniseian grammar.[45][edit] Mongolic theories
Some scholars, including Paul Pelliot and Byambyn Rinchen,[46] insisted on a Mongolic origin. Now, Hunnu or Hun (means "person" in Mongolian) empire are more commonly used in Mongolia. The Mongolian government celebrated the 2220th anniversary of the Foundation of Mongolia's Statehood—the Hun Empire in 2011.[47][48][edit] Theories on multi-ethnicity
Albert Terrien de Lacouperie considered them to be multi-component groups.[49] Many scholars believe the Xiongnu confederation was a mixture of different ethno-linguistic groups, and that their main language (as represented in the Chinese sources) and its relationships, have not yet been satisfactorily determined.[50][edit] Language isolate theories
The Turkologist Gerhard Doerfer has denied any possibility of a relationship between the Xiongnu language and any other known language and rejected in the strongest terms any connection with Turkish or Mongolian.[51][edit] Identity, archaeology, and genetics
The original geographic location of the Xiongnu is disputed among steppe archaeologists. Since the 1960s, the geographic origin of the Xiongnu has attempted to be traced through an analysis of Early Iron Age burial constructions. No region has been proven to have mortuary practices that clearly match that of the Xiongnu.[52][edit] Archaeology
In the 1920s, Pyotr Kozlov's excavations of the royal tombs at Noin-Ula in northern Mongolia that date to around the 1st century CE, provided a glimpse into the lost world of the Xiongnu. Other archaeological sites have been unearthed in Inner Mongolia and elsewhere; they represent the Neolithic and historical periods of the Xiongnu's history.[53] Those included the Ordos culture, many of them had been identified as the Xiongnu cultures. The region was occupied predominantly by peoples showing Mongoloid features, known from their skeletal remains and artifacts. Portraits found in the Noin-Ula excavations demonstrate other cultural evidences and influences, showing that Chinese and Xiongnu art have influenced each other mutually. Some of these embroidered portraits in the Noin-Ula kurgans also depict the Xiongnu with long braided hair with wide ribbons, which are seen to be identical with the Turkic Ashina clan hair-style.[54] Well-preserved bodies in Xiongnu and pre-Xiongnu tombs in the Mongolian Republic and southern Siberia show both 'Mongoloid' and 'Caucasian' features[55] but are predominantly Mongoloid with some admixture of European physical stock, nonetheless the Xiongnu shared many cultural traits with their Indo-European neighbors, such as horse racing, sword worship.[56] Analysis of skeletal remains from sites attributed to the Xiongnu provides an identification of dolichocephalic Mongoloid, ethnically distinct from neighboring populations in present-day Mongolia.[57] Russian and Chinese anthropological and craniofacial studies show that the Xiongnu were physically very heterogenous, with six different population clusters showing different degrees of Mongoloid and Caucasoid physical traits. These clusters point to significant cross-regional migrations (both east to west and west to east) that likely started in the Neolithic period and continued to the medieval/Mongolian period.[58]Presently, there exist four fully excavated and well documented cemeteries: Ivolga,[59] Dyrestui,[60] Burkhan Tolgoi,[61][62] and Daodunzi.[63][64] Additionally thousands of tombs have been recorded in Transbaikalia and Mongolia. In addition to these, the Tamir 1 excavation site from a 2005 Silkroad Arkanghai Excavation Project is the only Xiongnu cemetery in Mongolia to be fully mapped in scale.[65] Tamir 1 was located on Tamiryn Ulaan Khoshuu, a prominent granitic outcrop near other cemeteries of the Neolithic, Bronze Age, and Mongol periods.[66] Important finds at the site included a lacquer bowl, glass beads, and three TLV mirrors. Archaeologists from this project believe that these artifacts paired with the general richness and size of the graves suggests that this cemetery was for more important or wealthy Xiongnu individuals.[66] The TLV mirrors are of particular interest. Three mirrors were acquired from three different graves at the site. The mirror found at feature 160 is believed to be a low-quality, local imitation of a Han mirror, while the whole mirror found at feature 100 and fragments of a mirror found at feature 109 are believed to belong to the classical TLV mirrors and date back to the Xin Dynasty or the early to middle Eastern Han period.[67] The archaeologists have chosen to, for the most part, refrain from positing anything about Han-Xiongnu relations based on these particular mirrors. However, they were willing to mention the following: "There is no clear indication of the ethnicity of this tomb occupant, but in a similar brick-chambered tomb of late Eastern Han period at the same cemetery, archaeologists discovered a bronze seal with the official title that the Han government bestowed upon the leader of the Xiongnu. The excavators suggested that these brick chamber tombs all belong to the Xiongnu (Qinghai 1993)."[67]
Classifications of these burial sites make distinction between two prevailing type of burials: "(1). monumental ramped terrace tombs which are often flanked by smaller "satellite" burials and (2) 'circular' or 'ring' burials."[68] Some scholars consider this a division between "elite" graves and "commoner" graves. Other scholars, find this division too simplistic and not evocative of a true distinction because it shows "ignorance of the nature of the mortuary investments and typically luxuriant burial assemblages [and does not account for] the discovery of other lesser interments that do not qualify as either of these types."[69]
[edit] Genetics
| This article may contain original research. (November 2008) |
A majority (89%) of the Xiongnu mtDNA sequences can be classified as belonging to Asian haplogroups, and nearly 11% belong to European haplogroups. This finding indicates that the contacts between European and Asian populations were anterior to the Xiongnu culture, and it confirms results reported for two samples from an early 3rd century BC. Scytho–Siberian population (Clisson et al. 2002).
Another study[71] from 2004 screened ancient samples from the Egyin Gol necropolis for the Y-DNA Tat marker. The Egyin Gol necropolis, located in northern Mongolia in the region of Lake Baikal, is ~2300 years old and belongs to the Xiongnu culture. This Tat-polymorphism is a biallelic marker – that defines the N1c (N3-Tat) Y-DNA haplogroup – what has so far been observed only in populations from Asia and northern Europe. It reaches its highest frequency in Yakuts and northern Uralic peoples, with significant parts also in Buryats and northeastern Siberian populations. Opinions differ about whether the geographic origin of the T-C mutation lies in Asia or northern Eurasia. Zerjal et al. suggested that this mutation first arose in the populations of Central Asia; they proposed Mongolia as a candidate location for the origin of the T-C polymorphism. In contrast, for Lahermo et al. the wide distribution of the mutation in north Eurasian populations suggests that it arose in northern Eurasia. According to them, the estimated time of the C mutation is ~2400–4440 years ago. (According to some more recent researches of the Y-DNA Hg N the presence of N1c and N1b in modern Siberian and other Eurasian populations is considered to reflect an ancient substratum, probably speaking Uralic languages.)[72][73][74][75] Concerning the Xiongnu people, two of them from the oldest section harboured the mutation, confirming that the Tat polymorphism already existed in Mongolia 2300 years ago. The next archaeogenetical occurrence of this N-Tat ancient DNA was found in Hungary among the so-called Homeconqueror Hungarians.[76] Also three Yakuts' aDNA from the 15th century, and of two from the late 18th century were this haplogroup.[77] Additionally two mtDNA sequence matches revealed in this work suggest that the Xiongnu tribe under study may have been composed of some of the ancestors of the present-day Yakut population.
Another study of 2006,[78] using genetic and archeological data from a Siberian grave of Pokrovsk recently discovered near the Lena River and dated from 2,400 to 2,200 years B.P., as well as modern Buryats, Khanty, Mansi, Evenk, and Yakuts, provided evidence for the existence of early contact between autochthonous hunters of the Siberian taiga and nomadic horse breeders from the Altai-Baikal area (Mongolia and Buryatia). The similarity of the mitochondrial haplotype of the Pokrovsk subject with a woman of the Egyin Gol necropolis of the 2nd/3rd century AD ( mtDNA D haplogroup) shows that this contact would have occurred by the end of the Xiongnu period, and possibly prior to the 3rd century BC.. This contact could have been through either the expansion of the Xiongnu and other steppe peoples westwards to new areas of Siberia, or northwards along riverways. The Yenisei (Ienissei) river in particular contributed to extensive east-west gene flow. The combined evidence demonstrates the close relationship between the Xiongnu and the Siberian populations.
Another 2006 study observed genetic similarity among Mongolian samples from different periods and geographic areas including 2,300-year-old Xiongnu population of the Egyin Gol Valley. This results supports the hypothesis that the succession over time of different Turkic and Mongolian tribes in the current territory of Mongolia resulted in cultural rather than genetic exchanges. Furthermore, it appears that the Yakuts probably did not find their origin among the Xiongnu tribes as previously hypothesised.[79]
A research study of 2006[80] focused on Y-DNAs of the Egyin Gol site, and besides the confirmation of the above mentioned two N3-Tats, it also identified a Q-M242 haplogroup from the middle period and a C-M130 haplogroup from the later (2nd century AD). The Q-M242 is one of the haplogroups of the indigenous peoples of the Americas (though this is not this subclade), and minor across Eurasia. Only two groups in the Old World are high majority Q-M242 groups. These are the Samoyedic Selkups and the Yeniseian Kets. They live in western and middle Siberia, together with the Ugric Khantys. The Kets originally lived in southern Siberia. The Uralic-Samoyedics were an old people of the Sayan-Baikal region, migrated northwest around the 1st/2nd century AD. According to the Uralistic literature[81] the swift migration and disjunction of the Samoyedic peoples might be connected to a heavy warring in the region, probably due to the dissolution of the Xiongnu Empire in the period of the Battle of Ikh Bayan. The mutation defining this haplogroup C-M130, is restrained in North and Eastern-Asia and in America (Bergen et al. 1998. 1999.) (Lell et al. 2002.). The highest frequencies of Haplogroup C3 are found among the populations of Mongolia and the Russian Far East, where it is generally the modal haplogroup. Haplogroup C3 is the only variety of Haplogroup C-M130 to be found among Native Americans, among whom it reaches its highest frequency in Na-Dené populations.
A research project of 2007 (Yi Chuan, 2007[82]) was aimed at the genetic affinities between Tuoba Xianbei and Xiongnu populations. Some mtDNA sequences from Tuoba Xianbei remains in Dong Han period were analyzed. Comparing with the published data of Xiongnu, the results indicated that the Tuoba Xianbei presented some close affinities to the Xiongnu, which implied that there was a gene flow between Tuoba Xianbei and Xiongnu during the two southward migrations.
A recent examination[83] in a Xiongnu cemetery in Duurlig Nars revealed a Western Eurasian male with maternal U2e1 and paternal R1a1 haplogroups and two other DNAs: a female with mtDNA haplogroup D4 and a male with Y-haplogroup C3 and mtDNA haplogroup D4.
A study of 2010 [84] analysed six human remains of a nomadic group, excavated from Pengyang, Northern China. From the mtDNA, six haplotypes were identified as three haplogroups: C, D4 and M10. The analyses revealed that these individuals were closely associated with the ancient Xiongnu and modern northern Asians. The analysis of Y chromosomes from four male samples that were typed as haplogroup Q-M242 indicated that these people had originated in Siberia.
[edit] Material culture
[edit] Artistic distinctions
| This section relies largely or entirely upon a single source. (December 2012) |
Xiongnu art is harder to distinguish from Saka art. There was a similarity present in stylistic execution, but Xiongnu art and Saka art did often differ in terms of iconography. Saka art does not appear to have included predation scenes, especially with dead prey, or same-animal combat. Additionally, Saka art included elements not common to Xiongnu iconography, such as a winged, horned horse.[89] The two cultures also used two different bird heads. Xiongnu depictions of birds have a tendency to have a moderate eye and beak and have ears, while Saka birds have a pronounced eye and beak and no ears.[90] Some scholars claim these differences are indicative of cultural differences. Scholar Sophia-Karin Psarras claims that Xiongnu images of animal predation, specifically tiger plus prey, is spiritual, representative of death and rebirth, and same-animal combat is representative of the acquisition of or maintenance of power.[90]
[edit] Rock art and writing
The rock art of the Yinshan and Helanshan is dated from the 9th millennium BC to 19th century. It consists mainly of engraved signs (petroglyphs) and only minimally of painted images.[91]Excavations conducted between 1924–1925, in Noin-Ula kurgans located in Selenga River in the northern Mongolian hills north of Ulan Bator, produced objects with over twenty carved characters, which were either identical or very similar to that of to the runic letters of the Turkic Orkhon script discovered in the Orkhon Valley. From this a some scholars hold that the Xiongnu had a script similar to Eurasian runiform and this alphabet itself served as the basis for the ancient Turkic writing.[92]
- 2nd century BC – 2nd century AD, characters of Hun- Syanbi script (Mongolia and Inner Mongolia), N. Ishjamts, "Nomads In Eastern Central Asia", in the History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume 2, Fig 5, p. 166, UNESCO Publishing, 1996, ISBN 92-3-102846-4
- 2nd century BC – 2nd century AD, characters of Hun- Syanbi script (Mongolia and Inner Mongolia), N. Ishjamts, "Nomads In Eastern Central Asia", in the History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume 2, Fig 5, p. 166, UNESCO Publishing, 1996, ISBN 92-3-102846-4
[edit] See also
- Historic states represented in Turkish presidential seal
- Ethnic groups in Chinese history
- List of Mongolian monarchs
- Nomadic empire
[edit] References
- ^ Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (2nd edition, 2010). The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Cambridge University Press. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-521-12433-1.
- ^ Adas 2001: 88
- ^ a b Beckwith 2009: 404-405, nn. 51-52.
- ^ a b Harmatta 1999: 488
- ^ a b Jankowski 2006: 27
- ^ Di Cosmo, 2004, pg 166
- ^ Yuri Pines, The Everlasting Empire: The Political Culture of Ancient China and Its Imperial Legacy, Princeton University Press, 2012, p.37. ISBN 1400842271, 9781400842278.
- ^ John Man, Attila: the barbarian king who challenged Rome, Bantam, 2005, p.62. University of Michigan. ISBN 0593052919, 9780593052914.
- ^ Vaissière 2006
- ^ di Cosmo 2004: 186
- ^ Di Cosmo 2002, 2.
- ^ a b c Di Cosmo 2002, 129.
- ^ Di Cosmo 1999, 892–893.
- ^ a b Di Cosmo 1999, 892–893 & 964.
- ^ Beckwith 2009, 71.
- ^ Beckwith 2009, 71–72.
- ^ Barfield 1989
- ^ di Cosmo 1999: 885-966
- ^ a b Jerry Bentley, Old World Encounters: Cross-Cultural Contacts and Exchanges in Pre-Modern Times (New York: Oxford University Press, 1993), 36
- ^ a b Yü, Ying-shih (1986). "Han Foreign Relations". The Cambridge History of China, Volume 1: The Ch'in and Han Empires, 221 B.C. - A.D. 220. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 384. ISBN 0-521-24327-0.
- ^ a b c Barfield, Thomas J. (1981). "The Hsiung-nu imperial confederacy: Organization and foreign policy". The Journal of Asian Studies 41 (1): 48. JSTOR 2055601.
- ^ Grousset 1970
- ^ Grousset 1970: ch. 1, citing Kurakichi Shiratori ca. 1900
- ^ Yap,page liii
- ^ Grousset,page 20
- ^ Loewe 1974
- ^ This view was put forward to Wang Mang in AD 14: Han Shu (Beijing: Zhonghua shuju edition) 94B, p. 3824.
- ^ Sand-covered Hun City Unearthed. http://www.china.org.cn/english/travel/45103.htm
- ^ National Geographic Online. http://www.geographic.hu/index.php?act=napi&id=5207
- ^ Obrusánszky 2006
- ^ Ancient Hun Capital Bids for World Cultural Site. http://www.china.org.cn/english/travel/92329.htm
- ^ Thomas J. Barfield, 'The Perilous Frontier: Nomadic Empires and China, 221 BC to AD 1757',1989
- ^ Vaissière 2005
- ^ Pritsak 1959
- ^ Wink 2002: 60-61
- ^ Hucker 1975: 136
- ^ History of Northern Dynasties, vol. 99
- ^ Book of Zhou, vol. 50
- ^ Henning 1948
- ^ Klyashtorny 1964: 108
- ^ Gumilev: ch. 3, p. 3
- ^ Zuev 1960: 6-7
- ^ Sims-Williams 2004
- ^ Bailey 1985: 25-41
- ^ Vovin 2000
- ^ Ts. Baasansuren "The scholar who showed the true Mongolia to the world", Summer 2010 vol.6 (14) Mongolica, pp.40
- ^ http://english.news.mn/content/26062.shtml
- ^ http://www.president.mn/eng/newsCenter/viewNews.php?newsId=288
- ^ Geng 2005
- ^ Di Cosmo 2004: 165
- ^ Di Cosmo 2004: 164
- ^ Honeychurch, William. "Thinking Political Communities: The State and Social Stratification among Ancient Nomads of Mongolia". The Anthropological Study of Class and Consciousness: 47.
- ^ Zhang et al. 2001: 176–225
- ^ Camilla Trever, "Excavations in Northern Mongolia (1924–1925)", Leningrad: J. Fedorov Printing House, 1932 [1]
- ^ The Great Empires of the Ancient World - Thomas Harrison - 2009 - 288 page
- ^ Ancient bronzes, ceramics, and seals: the Nasli M. Heeramaneck Collection of ancient Near Eastern, central Asiatic, and European art, gift of the Ahmanson Foundation [2]
- ^ Fu ren da xue (Beijing, China), S.V.D. Research Institute, Society of the Divine Word - 2003 [3]
- ^ Tumen D., "Anthropology of Archaeological Populations from Northeast Asia [4]
- ^ A. V. Davydova, Ivolginskii arkheologicheskii kompleks II. Ivolginskii mogil’nik. Arkheologicheskie pamiatniki Siunnu 2 (Sankt-Peterburg 1996). А. В. Давыдова, Иволгинский археологи-ческий комплекс II. Иволгинский могильник. Археологические памятники Сюнну 2 (Санкт-Петербург 1996).
- ^ S. S. Miniaev, Dyrestuiskii mogil’nik. Arkheologicheskie pamiatniki Siunnu 3 (Sankt-Peterburg 1998). С. С. Миняев, Дырестуйский могильник. Археологические памятники Сюнну 3 (Санкт-Петербург 1998).
- ^ Ts. Törbat, Keramika khunnskogo mogil’nika Burkhan-Tolgoi. Erdem shinzhilgeenii bichig. Arkheologi, antropologi, ugsaatan sudlal 19,2003, 82–100. Ц. Тѳрбат, Керамика хуннского могильника Бурхан-Толгой. Эрдэм шинжилгээний бичиг. Археологи, антропологи, угсаатан судлал 19, 2003, 82–100.
- ^ Ts. Törbat, Tamiryn Ulaan khoshuuny bulsh ba Khünnügiin ugsaatny büreldekhüünii asuudald. Tükhiin setgüül 4, 2003, 6–17. Ц. Төрбат, Тамирын Улаан хошууны булш ба Хүннүгийн угсаатны бүрэлдэхүүний асуудалд. Түүхийн сэтгүүл 4, 2003, 6–17.
- ^ Ningxia wenwu kaogu yanjiusuo 寧夏文物考古研究所/Zhongguo shehui kexueyuan kaogusuo Ningxia kaoguzu 中國社會科學院考古所寧夏考古組/Tongxin xian wenwu guanlisuo 同心縣 文物管理所, Ningxia Tongxin Daodunzi Xiongnu mudi 寧夏同心倒墩子匈奴墓地. Kaogu xuebao 1988, 3, 333–356.
- ^ Miller, Bryan (2011). In Jan Bemmann. Xiongnu Archaeology. Bonn: Vor- und Fruhgeschichtliche Archaologie Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universitat Bonn. ISBN 978-3-936490-14-7 Check
|isbn=value (help). - ^ Purcell, David. "Maps of the Xiongnu Cemetery at Tamiryn Ulaan Khoshuu, Ogii nuur, Arkhangai Aimag, Mongolia". The Silk Road 9: 143–145.
- ^ a b Purcell, David; Kimberly Spurr. "Archaeological Investigations of Xiongnu Sites in the Tamir River Valley". The Silk Road 4 (1): 20–31.
- ^ a b Lai, Guolong. "The Date of the TLV Mirrors from the Xiongnu Tombs". The Silk Road 4 (1): 34–43.
- ^ Miller, Bryan (2011). In Jan Bemmann. Xiongnu Archaeology. Bonn: Vor- und Fruhgeschichtliche Archaologie Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universitat Bonn. p. 23. ISBN 978-3-936490-14-7 Check
|isbn=value (help). - ^ Miller, Bryan (2011). In Jan Bemmann. Xiongnu Archaeology. Bonn: Vor- und Fruhgeschichtliche Archaologie Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universitat Bonn. p. 24. ISBN 978-3-936490-14-7 Check
|isbn=value (help). - ^ Genome News Network 2003
- ^ Keyser-Tracqui, C (2004). "Does the Tat polymorphism originate in northern Mongolia?". International Congress Series 1261: 325. doi:10.1016/S0531-5131(03)01701-1.
- ^ Derenko, Miroslava; Malyarchuk, Boris; Denisova, Galina; Wozniak, Marcin; Grzybowski, Tomasz; Dambueva, Irina; Zakharov, Ilia (2007). "Y-chromosome haplogroup N dispersals from south Siberia to Europe". Journal of Human Genetics 52 (9): 763–70. doi:10.1007/s10038-007-0179-5. PMID 17703276.
- ^ Rootsi, Siiri; Zhivotovsky, Lev A; Baldovič, Marian; Kayser, Manfred; Kutuev, Ildus A; Khusainova, Rita; Bermisheva, Marina A; Gubina, Marina et al. (2006). "A counter-clockwise northern route of the Y-chromosome haplogroup N from Southeast Asia towards Europe". European Journal of Human Genetics 15 (2): 204–11. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201748. PMID 17149388.
- ^ Kharkov VN, Stepanov VA, Medvedeva OF, et al. (May 2007). "[Gene pool differences between northern and southern Altaians inferred from the data on Y-chromosomal haplogroups]". Genetika (in Russian) 43 (5): 675–87. PMID 17633562. (English title: Russian Journal of Genetics)
- ^ Lappalainen, T.; Laitinen, V.; Salmela, E.; Andersen, P.; Huoponen, K.; Savontaus, M.-L.; Lahermo, P. (2008). "Migration Waves to the Baltic Sea Region". Annals of Human Genetics 72 (Pt 3): 337–48. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2007.00429.x. PMID 18294359.
- ^ Csányi et al. 2008
- ^ F.-X. Ricaut, O. Safedoseva, C. Keyser-Tracqui, E. Crubézy, B. Ludes, in press. Genetic analysis of human remains found in two medieval Yakut graves (At-Dabaan site, 18th century), Int. J. Legal. Med.
- ^ Amory S, Crubézy E, Keyser C, Alekseev AN, Ludes B (October 2006). "Early influence of the steppe tribes in the peopling of Siberia". Human Biology 78 (5): 531–49. doi:10.1353/hub.2007.0001. PMID 17506285.
- ^ Keyser-Tracqui C, Crubézy E, Pamzsav H, Varga T, Ludes B (October 2006). "Population origins in Mongolia: genetic structure analysis of ancient and modern DNA". American Journal of Physical Anthropology 131 (2): 272–81. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20429. PMID 16596591.
- ^ Petkovski 2006: 138-140
- ^ Helimski
- ^ Yu CC, Xie L, Zhang XL, Zhou H, Zhu H (October 2007). "[Genetic analyses on the affinities between Tuoba Xianbei and Xiongnu populations]". Yi Chuan (in Chinese) 29 (10): 1223–9. PMID 17905712.
- ^ A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 January.
- ^ Ancient DNA from nomads in 2500-year-old archeological sites of Pengyang, China. Journal of Human Genetics, Feb 2010
- ^ Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 55–236.
- ^ Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 101.
- ^ Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 101–102.
- ^ Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 229.
- ^ Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 95,102–103.
- ^ a b Psarras, Sophia-Karin (2003). "Han and Xiongnu: A Reexamination of Cultural and Political Relations". Monumenta Serica 51: 102–103.
- ^ Demattè 2006
- ^ Ishjamts 1996: 166
[edit] Bibliography
[edit] Primary sources
- Ban Gu et al., Book of Han, esp. vol. 94, part 1, part 2.
- Fan Ye et al., Book of Later Han, esp. vol. 89.
- Sima Qian et al., Records of the Grand Historian, esp. vol. 110.
[edit] Works consulted
- Adas, Michael. 2001. Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History, American Historical Association/Temple University Press.
- Bailey, H[arold] W. 1985. Indo-Scythian Studies: being Khotanese Texts, VII. Cambridge Univ. Press. (Reviewed here)
- Barfield, Thomas. 1989. The Perilous Frontier. Basil Blackwell.
- Beckwith, Christopher I. 2009. Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13589-2
- Brosseder, Ursula, and Bryan Miller. Xiongnu Archaeology: Multidisciplinary Perspectives of the First Steppe Empire in Inner Asia. Bonn: Freiburger Graphische Betriebe- Freiburg, 2011.
- Csányi, B. et al. 2008. Y-Chromosome Analysis of Ancient Hungarian and Two Modern Hungarian-Speaking Populations from the Carpathian Basin. Annals of Human Genetics, 2008 March 27, 72(4): 519-534.
- Demattè, Paola. 2006. Writing the Landscape: Petroglyphs of Inner Mongolia and Ningxia Province (China). In: Beyond the steppe and the sown: proceedings of the 2002 University of Chicago Conference on Eurasian Archaeology, edited by David L. Peterson et al. Brill. Colloquia Pontica: series on the archaeology and ancient history of the Black Sea area; 13. 300-313. (Proceedings of the First International Conference of Eurasian Archaeology, University of Chicago, May 3–4, 2002.)
- Davydova, Anthonina. The Ivolga archaeological complex. Part 1. The Ivolga fortress. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 1. St Petersburg, 1995.
- Davydova, Anthonina. The Ivolga archaeological complex. Part 2. The Ivolga cemetery. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 2. St Petersburg, 1996.
- (Russian) Davydova, Anthonina & Minyaev Sergey. The complex of archaeological sites near Dureny village. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 5. St Petersburg, 2003.
- Davydova, Anthonina & Minyaev Sergey. The Xiongnu Decorative bronzes. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 6. St Petersburg, 2003.
- Di Cosmo, Nicola. 1999. The Northern Frontier in Pre-Imperial China. In: The Cambridge History of Ancient China, edited by Michael Loewe and Edward Shaughnessy. Cambridge University Press.
- Di Cosmo, Nicola. 2004. Ancient China and its Enemies: The Rise of Nomadic Power in East Asian History. Cambridge University Press. (First paperback edition; original edition 2002)
- (Chinese) Geng, Shi-min [耿世民]. 2005. 阿尔泰共同语、匈奴语探讨 (On Altaic Common Language and Xiongnu Language). <<语言与翻译(汉文版)>> (Yu yan yu fan yi, Language and Translation), 2005年 第02期. Wulumuqi (Ürümqi). ISSN: 1001-0823. WorldCat id=123501525. Database citation page for this article
- Genome News Network. 2003 July 25. "Ancient DNA Tells Tales from the Grave"
- Grousset, René. 1970. The empire of the steppes: a history of central Asia. Rutgers University Press.
- (Russian) Gumilev L. N. 1935. История народа Хунну (History of the Hunnu people).
- Hall, Mark & Minyaev, Sergey. Chemical Analyses of Xiong-nu Pottery: A Preliminary Study of Exchange and Trade on the Inner Asian Steppes. In: Journal of Archaeological Science (2002) 29, pp. 135–144
- Harmatta, János. 1999. Conclusion. In: History of civilizations of Central Asia. Volume 2: The Development of Sedentary and Nomadic Civilizations, 700 bc to ad 250; Edited by János Harmatta et al. UNESCO. ISBN 92-3-102846-4. 485-493.
- (Hungarian) Helimski, Eugen. "A szamojéd népek vázlatos története" (Short History of the Samoyedic peoples). In: The History of the Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic Peoples. 2000, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary.
- Henning W. B. 1948. The date of the Sogdian ancient letters. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies (BSOAS), 12(3-4): 601–615.
- Hill, John E. (2009) Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE. BookSurge, Charleston, South Carolina. ISBN 978-1-4392-2134-1. (Especially pp. 69–74)
- Hucker, Charles O. 1975. China's Imperial Past: An Introduction to Chinese History and Culture. Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-2353-2
- N. Ishjamts. 1999. Nomads In Eastern Central Asia. In: History of civilizations of Central Asia. Volume 2: The Development of Sedentary and Nomadic Civilizations, 700 bc to ad 250; Edited by Janos Harmatta et al. UNESCO. ISBN 92-3-102846-4. 151-170.
- Jankowski, Henryk. 2006. A historical-etymological dictionary of pre-Russian habitation names of the Crimea. Brill. Handbuch der Orientalistik [HdO], 8: Central Asia; 15. ISBN 90-04-15433-7.
- (Russian) Kradin N.N., "Hun Empire". Acad. 2nd ed., updated and added., Мoscow: Logos, 2001, ISBN 5-94010-124-0
- (Russian) Kiuner (Kjuner, Küner) [Кюнер], N.V. 1961. Китайские известия о народах Южной Сибири, Центральной Азии и Дальнего Востока (Chinese reports about peoples of Southern Siberia, Central Asia, and Far East). Мoscow.
- (Russian) Klyashtorny S.G. [Кляшторный С.Г.]. 1964. Древнетюркские рунические памятники как источник по истории Средней Азии. (Ancient Türkic runiform monuments as a source for the history of Central Asia). Moscow: Nauka.
- (German) Liu Mau-tsai. 1958. Die chinesischen Nachrichten zur Geschichte der Ost-Türken (T'u-küe). Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz.
- Loewe, Michael. 1974. The campaigns of Han Wu-ti. In: Chinese ways in warfare, ed. Frank A. Kierman, Jr., and John K. Fairbank. Harvard Univ. Press.
- Minyaev, Sergey. On the origin of the Xiongnu // Bulletin of International association for the study of the culture of Central Asia, UNESCO. Moscow, 1985, № 9.
- Minyaev, Sergey. News of Xiongnu Archaeology // Das Altertum, vol. 35. Berlin, 1989.
- Miniaev, Sergey. "Niche Grave Burials of the Xiong-nu Period in Central Asia", Information Bulletin, Inter-national Association for the Cultures of Central Asia 17(1990): 91-99.
- Minyaev, Sergey. The excavation of Xiongnu Sites in the Buryatia Republic// Orientations, vol. 26, n. 10, Hong Kong, November 1995.
- Minyaev, Sergey. Les Xiongnu// Dossiers d' archaeologie, # 212. Paris 1996.
- Minyaev, Sergey. Archaeologie des Xiongnu en Russie: nouvelles decouvertes et quelques Problemes. In: Arts Asiatiques, tome 51, Paris, 1996.
- Minyaev, Sergey. The origins of the "Geometric Style" in Hsiungnu art // BAR International series 890. London, 2000.
- Minyaev, Sergey. Art and archeology of the Xiongnu: new discoveries in Russia. In: Circle of Iner Asia Art, Newsletter, Issue 14, December 2001, pp. 3–9
- Minyaev, Sergey & Smolarsky Phillipe. Art of the Steppes. Brussels, Foundation Richard Liu, 2002.
- (Russian) Minyaev, Sergey. Derestuj cemetery. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 3. St-Petersburg, 1998.
- Miniaev, Sergey & Sakharovskaja, Lidya. Investigation of a Xiongnu Royal Tomb in the Tsaraam valley, part 1. In: Newsletters of the Silk Road Foundation, vol. 4, no.1, 2006.
- Miniaev, Sergey & Sakharovskaja, Lidya. Investigation of a Xiongnu Royal Tomb in the Tsaraam valley, part 2. In: Newsletters of the Silk Road Foundation, vol. 5, no.1, 2007.
- (Russian) Minyaev, Sergey. The Xiongnu cultural complex: location and chronology. In: Ancient and Middle Age History of Eastern Asia. Vladivostok, 2001, pp. 295–305.
- (Hungarian) Obrusánszky, Borbála. 2006 October 10. Huns in China (Hunok Kínában) 3.
- (Hungarian) Obrusánszky, Borbála. 2009. Tongwancheng, city of the southern Huns. Transoxiana, August 2009, 14. ISSN 1666-7050.
- (French) Petkovski, Elizabet. 2006. Polymorphismes ponctuels de séquence et identification génétique: étude par spectrométrie de masse MALDI-TOF. Strasbourg: Université Louis Pasteur. Dissertation
- (Russian) Potapov L.P. [Потапов, Л. П.] 1969. Этнический состав и происхождение алтайцев (Etnicheskii sostav i proiskhozhdenie altaitsev, Ethnic composition and origins of the Altaians). Leningrad: Nauka. Facsimile in Microsoft Word format.
- (German) Pritsak O. 1959. XUN Der Volksname der Hsiung-nu. Central Asiatic Journal, 5: 27-34.
- Psarras, Sophia-Karin. "HAN AND XIONGNU: A REEXAMINATION OF CULTURAL AND POLITICAL RELATIONS (I)." Monumenta Serica. 51. (2003): 55-236. Web. 12 Dec. 2012. <http://www.jstor.org/stable/40727370>.
- Sims-Williams, Nicholas. 2004. The Sogdian ancient letters. Letters 1, 2, 3, and 5 translated into English.
- (Russian) Talko-Gryntsevich, Julian. Paleo-Ethnology of Trans-Baikal area. In: Archaeological sites of the Xiongnu, vol. 4. St Petersburg, 1999.
- Taskin V.S. [Таскин В.С.]. 1984. Материалы по истории древних кочевых народов группы Дунху (Materials on the history of the ancient nomadic peoples of the Dunhu group). Moscow.
- (French) Vaissière, Étienne de la. 2005. Huns et Xiongnu. Central Asiatic Journal, 49(1): 3-26.
- Vaissière, Étienne de la. 2006. Xiongnu. Encyclopædia Iranica online.
- Vovin, Alexander. 2000. Did the Xiongnu speak a Yeniseian language? Central Asiatic Journal, 44(1): 87–104.
- Wink, A. 2002. Al-Hind: making of the Indo-Islamic World. Brill. ISBN 0-391-04174-6
- Yap, Joseph P. (2009). "Wars with the Xiongnu: A translation from Zizhi tongjian". AuthorHouse. ISBN 978-1-4490-0604-4
- (Chinese) Zhang, Bibo, and Dong, Guoyao [张碧波, 董国尧], eds. 2001. 中国古代北方民族文化史 (Zhongguo Gudai Beifang Minzu Wenhuashi = Cultural History of Ancient Northern Ethnic Groups in China). Harbin: Heilongjiang People's Press. ISBN 7-207-03325-7
- (Russian) Zuev, Yu. A. [Ю. Л. Зуев] 1960. К Этнической Истории Усуней (Ethnic history of the Wusuns). Trudy Instituta Istorii, Arkheologii i Etnografii, VIII. Alma-Ata: Akad. Nauk Kazakhskoi SSR.
[edit] Further reading
- (Russian) Потапов, Л. П. 1966. Этнионим Теле и Алтайцы. Тюркологический сборник, 1966: 233-240. Мoscow: Nauka. (Potapov L.P., The ethnonym "Tele" and the Altaians. Turcologica 1966: 233-240).
- Houle, J. and L.G. Broderick 2011 "Settlement Patterns and Domestic Economy of the Xiongnu in Khanui Valley, Mongolia", 137-152. In Xiongnu Archaeology: Multidisciplinary Perspectives of the First Steppe Empire in Inner Asia.
[edit] External links
- Downloadable article: "Evidence that a West-East admixed population lived in the Tarim Basin as early as the early Bronze Age" Li et al. BMC Biology 2010, 8:15. [5]
- Material Culture presented by University of Washington
- Encyclopedic Archive on Xiongnu
- Xiongnu Archaeology Enters a New Century
- The Xiongnu Empire
- The Silk Road Volume 4 Number 1
- The Silk Road Volume 9
- Gold Headdress from Aluchaideng
- Belt buckle, Xiongnu type, 3rd–2nd century B.C.
Huna people
Origin
The White Huna are of the stock of the Huns in fact as well as in name, however they do not mingle with any of the Huns known to us, for they occupy a land neither adjoining nor even very near to them; but their territory lies immediately to the north of Persia [...] They are not nomads like the other Hunnic peoples, but for a long period have been established in a goodly land.[23] Scholars believe that the name Hun is used to denote very different nomadic confederations. Ancient Chinese chroniclers, as well as Procopius, wrote various theories about the origins of the people:• They were descendants of the Yuezhi or Tocharian tribes who remained behind after the rest of the people fled the Xiongnu;
• They were descendants of the Kangju;
• They were a branch of the Tiele; or
• They were a branch of the Uar.
They were first mentioned by the Chinese, who described them as living in Dzungaria around AD 125[citation needed]. Chinese chronicles state that they were originally a tribe of the Yuezhi, living to the north of the Great Wall, and subject to the Rouran (Jwen-Jwen), as were some Turkic peoples at the time. Their original name was Hoa or Hoa-tun; subsequently they named themselves Ye-tha-i-li-to (厌带夷栗陁, or more briefly Ye-tha 嚈噠),[24] after their royal family, which descended from one of the five Yuezhi families which also included the Kushan.
They displaced the Scythians and conquered Sogdiana and Khorasan before AD 425. After that, they crossed the Syr Darya (Jaxartes) River and invaded Persian lands. In Persia, they were initially held off by Bahram Gur but around AD 483–85, they succeeded in making Persia a tributary state by defeating the Sassanid forces at the Battle of Herat where they killed the Sassanid king, Peroz I.[25] After a series of wars in the period AD 503–513, they were driven out of Persia and completely defeated in AD 557 by Khosrau I. Their polity thereafter came under the Göktürks and subsequent Western Turkic Khaganate.
The Hephtalites also invaded the regions Afghanistan and present-day Pakistan, succeeding in extending their domain to the Punjab region. Procopius claims that the White Huns lived in a prosperous territory, and that they were the only Huns with fair complexions. According to him, they did not live as nomads, did acknowledge a single king, observed a well-regulated constitution, and behaved justly towards neighboring states. He also describes the burial of their nobles in tumuli, accompanied by their closest associates. This practice contrasts with evidence of cremation among the Chionites in Ammianus and with remains found by excavators of the European Huns and remains in some deposits ascribed to the Chionites in Central Asia. Scholars believe that the White Huna constituted a second "Hunnish" wave who entered Bactria early in the 5th century AD, and who seem to have driven the Kidarites into Gandhara.[20] Newly-discovered ancient writings found in Afghanistan reveal that the Middle Iranian Bactrian language written in Greek script was not brought there by the White Huna, but was already present from Kushan times as the traditional language of administration in this region. There is also evidence of the use of a Turkic language under the White Huns. The Bactrian documents also attest several Turkic royal titles (such as Khagan), indicating an important influence of Turkic people on White Huns, although these could also be explained by later Turkic infiltration south of the Oxus.[20] According to Simokattes, they were Chionites who united under the White Huna as the "(Wusun) vultures descended on the people" around AD 460.
Yuezhi Theory
According to Mr. Adesh Katariya's evoluation All types of Hunas are Same and By mistake they called different Huna at different places. According to him ,Hun was a sub-tribe of ancient central Asian Tribe Gurjar/Gujjar, mostly known as Yuezhi by Chinese Scholers . These peoples were lived in North-east of Chinese Kingdoms( Present Ganshu provience of China). By 350 BCE, Chinese officials knew of three powerful groups of mounted, nomadic pastoral people north of China.1 (See map at right.) One of these groups, the Xiongnu (Hsiung-nu), was in the Ordos region2and most of Mongolia (including Inner Mongolia).3 To the east of the Xiongnu, in eastern Mongolia and the plains of Manchuria, there was the second group, the Donghu (Tung-hu).4 The third group, the Yuezhi (Yueh-chi), were west of the Ordos region, in the region of Gansu (Kansu).In 175 BCE The Xiongnu defeated the Yuezhi and dominated all of what is now the modern province of Xinjiang (Sinkiang). The leader of the Yuezhi was killed and his skull was made into a drinking cup. Following Chinese sources, a large part of the Yuezhi people therefore fell under the domination of the Xiongnu, and these may have been the ancestors of the Tocharian speakers attested in the 6th century CE. A very small group of Yuezhi fled south to the territory of the Proto-Tibetan Qiang and came to be known to the Chinese as the "Small Yuezhi". According to the Hanshu, they only numbered around 150 families After 40 years Gurjars (Yuezhi) made kingdoms , Kushana - Gurjars were made a big kingdom . Gurjar was a very complex Tribe divided by many sub - tribes like as Kushana, Khatana, Karahana(Kara- Huna), These Huna take the thrones of modern Afganistan , Pakistan, India and other central asian places and made many huna kingdoms . Now a days Huna peoples can be find in India as a Gotr of Gurjar Tribe.Religion
According to Song Yun, the Chinese Buddhist monk who visited the Hephthalite territory in 540 AD and "provides accurate accounts of the people, their clothing, the empresses and court procedures and traditions of the people and he states the White Huna did not recognize the Buddhist religion and they preached pseudo gods, and killed animals for their meat."[1] It is reported that the Hephtalites often destroyed Buddhist monasteries but were rebuilt by others. According to Xuanzang, the third Chinese pilgrim who visited the same areas as Song Yun about 100 years later, the capital of Chaghaniyan had five monasteries.[26] "In the Hephthalite dominion Buddism was predominant but there was also a religious sediment of Zoroastrianism, Manichaeism, and Nestorian Christianity."[3] Balkh had some 100 Buddhist monasteries and 3,000 monks. Outside the town was a large Buddhist monastery, later known as Naubahar.[26] Termez had 10 sangharamas (monasteries) and perhaps 1,000 monks.[26]History
The Central Asian Xionites consisted of four hordes in four cardinal directions. Northern Huna were the Black Huns, Southern Huna were the Red Huns, Eastern Huna were the Celestial Huns, and Western Huna were the White Huns or Hephthalites. This article mainly concerns the Alchon and their Indo-Hephthalite ruling-elite. They seem to have been part of the Hephthalite group, who established themselves in then Bharatvarsha and present day India by the first half of the 5th century. They sometimes call themselves "Hono" on their coins, but it seems that they are similar to the Huns who invaded the Western world.They appeared in Northwestern India and parts of eastern Iran. During their invasion, the Hunas managed to capture the Sassanian king Peroz I, and exchanged him for a ransom. They used the coins of the ransom to counter mark and copy them, thereby initiating a coinage inspired from Sassanian designs.[3]
The Bhishma Parva of the Mahabharata, supposed to have been edited around the 4th or 5th century, in one of its verses, mentions the Hunas with the Parasikas and other Mlechha tribes of the northwest including the Yavanas, Chinas, Kambojas, Darunas, Sukritvahas, Kulatthas etc.[4] According to Dr V. A. Smith, the verse is reminiscent of the period when the Hunas first came into contact with the Sassanian dynasty of Persia.[5]
Scholars believe that king Raghu, the hero of Kalidasa's Sanskrit play Raghuvamsha was in fact king Chandragupta Vikramaditya of the Gupta Dynasty. According to the epic,he had started a military expedition and after defeating and subjugating the local peoples along the way he reached the Parasikas of Sassanian Iran and defeated them after fierce fighting. Then he proceeded to north from Iran and reached river Vamkshu (or Oxus) where he battled with the Hunas. After conquering the Hunas, he crossed the Oxus and encountered the Kambojas, an ancient Iranian people who find frequent mention in South Asian texts.[6]
Brihat Katha Manjari of Kashmiri Pandit Kshmendra (11th century AD) also claims that king Vikramaditya had slaughtered the Shakas, Barbaras, Hunas, Kambojas, Yavanas, Parasikas and the Tusharas etc. and hence unburdened the earth of these sinful Mlechhas.[7] There is still another ancient Brahmanical text Katha-Saritsagara by Somadeva which also attests that king Vikramaditya had invaded the north-west tribes including the Kashmiras and had destroyed the Sanghas of the Mlechhas (reference to Sanghas here obviously alludes to the Sanghas of the Madrakas, Yaudheyas, Kambojas, Mallas or Malavas, Sibis, Arjunayans, Kulutas and Kunindas etc). Those who survived accepted his suzerainty and many of them joined his armed forces.[8]
These references suggest that the Guptas indeed had encounters with the Hunas from the north-west.
Skandagupta is stated to have repelled a Huna invasion in 455, but they continued to pressure South Asia's northwest frontier (present day Pakistan), and broke through into northern India by the end of the 5th century, hastening the disintegration of the Gupta Empire.
According to Litvinsky, the initial Huna or Alxon raids on Gandhara took place in the late 5th and early 6th century AD, upon the death of the Gupta ruler, Skandagupta (455–470), presumably led by the Tegin Khingila. M. Chakravary, based on Chinese and Persian histories believes that the Hunas conquered Gandhara from the Ki-to-lo (Kidarites) in c. 475 AD. Gandhara had been occupied by various Kidarite principalities from the early 4th century AD, but it is still a subject of debate as to whether rule was transferred from the Kidarites directly to the Hephthalites. It is known that the Huns invaded Gandhara and the Punjab from the Kabul valley after vanquishing the Kidarite principalities.
The Alchon ruler Toramana established his rule over Gandhara and western Punjab, and was succeeded by his son Mihirakula in 520 whose capital was Sakala or modern day Sialkot in the Pakistani Punjab. The Guptas continued to resist the Hunas, and allied with the rulers of the neighboring Indian states.
The Hunas suffered a defeat by Yasodharman of Malwa in 528, and by 542 Mihirakula had been driven off the plains of northern India, taking refuge in Kashmir, and he is thought to have died soon after. Mihirakula is remembered in contemporary Indian and Chinese histories for his cruelty and his destruction of temples and monasteries, with particular hostility towards Buddhism.
After the end of the 6th century little is recorded in India about the Huna. They made the matrimonial alliance with Gurjars and assimilated into the dominant Gurjar community. Huna is one minor gotra among Gurjars.
In northwestern India, the Rajputs formed "as a result of the merging of the Hephthalites and the Gujars with population from northwestern India."[9]
King Devapala of Pala dynasty of Bengal (810 AD −850 AD) is said to have invaded and received tributes from the Vindhyas, Dravidas, Hunas, Gurjaras and Kambojas in the West.[10]
The Hunas are mentioned in the Tibetan chronicle Dpag-bsam-ljon-bzah (The Excellent Kalpa-Vrksa), along people like the Yavanas, Kambojas, Tukharas, Khaqsas, Daradas etc.[11][12]
Religion
The Huns were fervent worshippers of the Vedic Sun God and Shiva [13]Sung Yun and Hui Sheng, who visited the chief of Hephthalite nomads at his summer residence in Badakshan and later in Gandhara, observed that they had no belief in the Buddhist law and they served a large number of divinities."[14]
Notes
- ^ Iaroslav Lebedynsky, "Les Nomades", p172.
- ^ Kurbanov, Aydogdy (2010). "The Hephthalites: Archaeological and Historical Analysis". p. 24. Retrieved 17 January 2013. "The Hūnas controlled an area that extended from Malwa in central India to Kashmir."
- ^ Source
- ^
- HrishIvidarbhah kantikasta~Nganah parata~Nganah. |
- uttarashchapare mlechchhA jana bharatasattama. || 63 ||
- YavanAshcha sa Kamboja Daruna mlechchha jatayah. |
- Sakahaddruhah Kuntalashcha Hunah Parasikas saha.|| 64 ||
- Tathaiva maradhAahchinastathaiva dasha malikah. |
- Kshatriyopaniveshashcha vaishyashudra kulani cha.|| 65 ||
- (Mahabharata 6.9.63–65) .
- ^ Early History of India, p 339, Dr V. A. Smith; See also Early Empire of Central Asia (1939), W. M. McGovern.
- ^ Raghuvamsa 4.65–71.
- ^ Brahata Katha 10.285-86.
- ^ Katha-Saritsagara, 18.1.76–78.
- ^ Kurbanov, Aydogdy (2010). "The Hephthalites: Archaeological and Historical Analysis". p. 243. Retrieved 11 January 2013. "As a result of the merging of the Hephthalites and the Gujars with population from northwestern India, the Rajputs (from Sanskrit “rajputra” – “son of the rajah”) formed."
- ^ Ancient India, 2003, p 650, Dr V. D. Mahajan; History and Culture of Indian People, The Age of Imperial Kanauj, p 50, Dr R. C. Majumdar, Dr A. D. Pusalkar.
- ^ Tho-gar yul dań yabana dań Kambodza dań Khasa dań Huna dań Darta dań...
- ^ Pag-Sam-Jon-Zang (1908), I.9, Sarat Chandra Das; Ancient Kamboja, 1971, p 66, H. W. Bailey.
- ^ History of civilizations of Central Asia, Volume 3 By Boris Abramovich Litvinovskiĭ Page 173
- ^ "The White Huns - The Hephthalites". Silkroad Foundation. Retrieved 11 January, 2013.
References
- Iaroslav Lebedynsky, "Les Nomades", Paris 2007, ISBN 978-2-87772-346-6
External links
- Hephthalite coins
- More Hephthalite coins
- Alchon Hunnic History and Coins of the Kashmir Smast Kingdom- Waleed Ziad